Multibeam Underwater Survey Plan Development
Developing a multibeam underwater survey plan involves comprehensive preparation and assessment to ensure accuracy, efficacité, et la qualité des données dans la cartographie du terrain sous-marin. Here is a step-by-step guide for establishing an effective survey plan:
1. Define Survey Objectives and Requirements
– Clearly outline the purpose of the survey, desired accuracy, and final deliverables, such as bathymetric maps, 3D models, or specific target identifications.
– Determine spatial and depth coverage requirements based on the application, whether for coastal surveys, harbor dredging, underwater construction, or seabed exploration.
2. Equipment Selection and Calibration
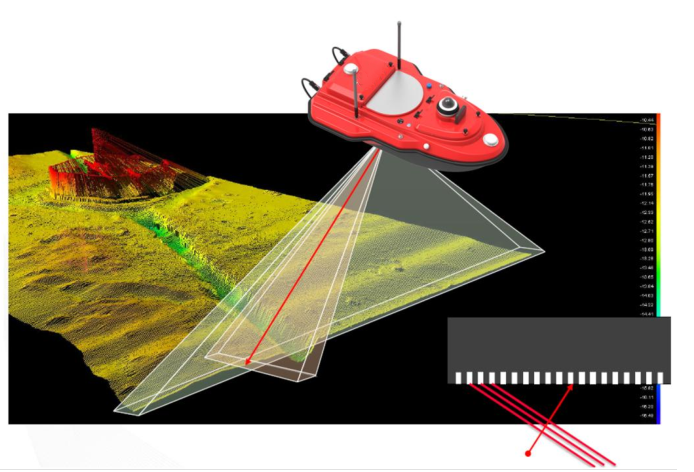
– Choose a suitable multibeam echo sounder based on the project’s depth, resolution, and environmental conditions (e.g., sediment type or water clarity).
– Equip the system with auxiliary equipment like Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) and an Inertial Navigation System (INS) to ensure precise positioning and stable data capture.
– Calibrate the multibeam sonar and all positioning equipment to ensure accuracy before deployment.
3. Environmental and Site Assessment
– Analyze the site’s characteristics, including water depth, seabed composition, currents, and potential obstacles, to tailor the approach.
– Consider environmental factors such as tides, weather, and daylight hours to minimize their impact on data collection and operational safety.
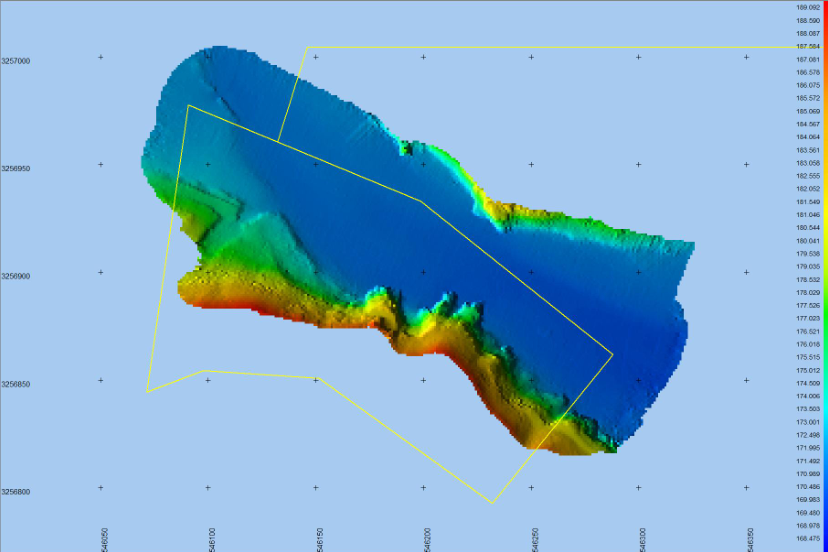
4. Survey Line Planning
– Develop a grid of survey lines with overlapping swaths to ensure full coverage of the survey area without data gaps.
– Calculate optimal line spacing based on depth and beam width, and establish ideal vessel speed to balance data quality with survey efficiency.
5. Data Collection Strategy
– Implement protocols for continuous, real-time monitoring of data quality, including tracking depth, positioning, and swath coverage.
– Set guidelines for managing unexpected conditions (e.g., sudden changes in water clarity or currents) that might affect data accuracy.
6. Data Processing Workflow
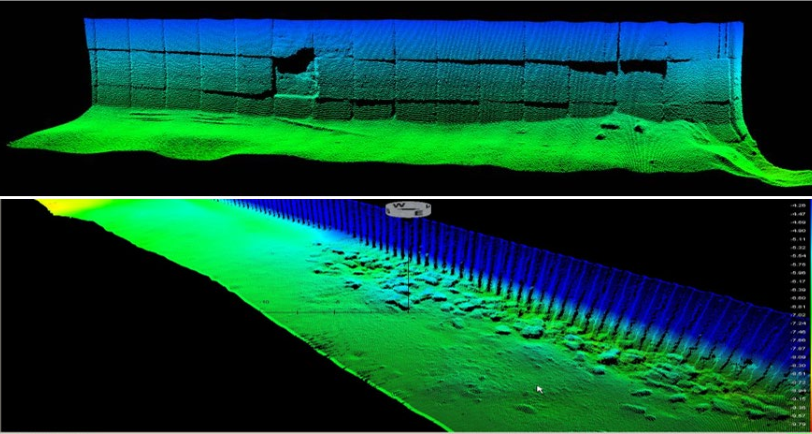
– Employ specialized software to process the collected point cloud data, performing filtering, noise reduction, and alignment.
– Generate the required deliverables, such as high-resolution bathymetric maps, digital terrain models (DTMs), or cross-sectional profiles.
7. Quality Assurance and Validation
– Establish quality control measures, including error analysis, calibration checks, and cross-referencing with other available datasets to validate accuracy.
– Conduct consistency checks between adjacent swaths and remove artifacts or anomalies to maintain data integrity.
8. Report Preparation and Deliverables
– Compile a detailed survey report with visual representations, charts, and analytical findings, summarizing key observations and measurements.
– Provide deliverables in the requested formats, ensuring compatibility with the client’s GIS or CAD software for further analysis.
9. Safety and Environmental Considerations
– Develop a comprehensive safety plan, particularly for deep-water or challenging environments, ensuring crew and equipment safety.
– Implement environmental safeguards to minimize impact, especially in ecologically sensitive areas, adhering to local and international regulations.
With meticulous planning and adherence to best practices, a multibeam underwater survey can yield precise and comprehensive data to support applications in marine engineering, environmental monitoring, and underwater mapping.
 Intelligent
Intelligent